반응형
Syntax
통사론은 구문론은 단어가 문장을 이루는 방법을 연구하는 언어학의 하위 분야이다.
1. Syntax Rules
- 올바른 구문 또는 문장을 생성하는 규칙
- word + syntactic rule + word = phrase
- phrase + syntactic rule + phrase = sentence
(예시)영어는 SVO 어순
- The President nominated a new Supreme Court justice (o)
- President The new Supreme a Court justice nominated (x)
(예시)한국어는 SOV 어순으로 구성되어있다.
- 대통령은 새 대법관을 지명했다.(o)
- 새 대법관을 대통령은 지명했다. (o)
- 대통령은 지명했다 새 대법관을 (의미는 해석 가능, 문법적은 x)
- 새 지명했다 대법관을 대통령은 (x)
- 어순이 다를 경우 완전히 다른 의미가 될 수 있다.
예시
- I mean what i say vs I say what i mean - 나는 망원경을 들고 있는 남자를 보았다 vs 망원경을 들고 있는 나는 남자를 보았다. - 구문 규칙은 문법적 관계를 결정해준다💡 한국어는 어순보다 조사에 의해 문법적 관계의 영향이 더 크다 → 한국어의 어순이 다른 언어에 비해 자유로운 이유
예시
- Your dog chased my cat vs. My cat chased your dog. - 네 강아지가 내 고양이를 쫒아왔다. vs 내 고양이가 네 강아지를 쫒아왔다. - 문장의 동사에따라서 문장 성분의 제약이 있다
- 단어의 그룹과 계급을 정해준다
예시
- The captain ordered the old men and women off the ship(2가지 해석 가능, 상황에 따라 결정)\ → 1. The captain ordered the [old [men and women]] off the ship.\ → 2. The captain ordered the [old men] and [women] off the ship.
2. 문법이 전제로 하고있지 않은 것
- 문법은 이전에 나왔던 문장에 기초하지 않는다
- 문법은 의미에 기초하지 않는다
- 문법은 진실성에 기초하지 않는다
예시
- Enormous crickets in pink socks danced at the prom. - Colorless green ideas sleep furiously - 문법은 틀리지만 의미해석이 가능한 문장있다.
3. 문장의 구조
"The child found the puppy"같은 간단한 문장도 컴퓨터는 1차원적으로 해석하기 때문에 문장의 의미를 이해하지 못한다
- 단지 Det-N-V-Det-N 처럼 한줄의 단어 나열로 알고있다
- 문장에서 의미가 있게 분할이 필요하다
-

Constituents(구성 요소) and Constituency Tests
- Constituents는 문장안에서의 자연스러운 그룹화 하는 것이다
- 예시. [[the] [child]] [[found] [[a] [puppy]]
- 구성 요소로 묶는 방법
- 혼자 사용이 가능한가
- a puppy는 가능, found a는 불가능
- 대명사로 대체 가능한가
- → “I found him in the park.” (a puppy)
→ “I found him in the park and Bill did too.” (found a puppy)
- → “I found him in the park.” (a puppy)
- 한개의 unit으로 이동이 가능한가
- The child found a puppy → A puppy was found by the child.
- 혼자 사용이 가능한가
4. Syntactic Categories(구문 범주)
- 문범적 오류 없이 대체로 표현이 가능한 것(명사구(NP), 동사구(VP)...)
예시
- NP(Noun + Phrase) : A bird, The woman who was laughing, It, John $\cdots$ - VP(Verb + Phrase) : ate the cake, slept $\cdots$ - Phrasal Categories(구 범주)
- NP (명사구): men, the man, the man with a telescope
- VP (동사구): sees, always sees, rarely sees the man, often sees the man with a, telescope, know who you are, slept on the bed
- PP (전치사구): over, nearly over, over the hill
- AdjP (형용사구): happy, very happy, very happy about winning
- AdvP (부사구): brightly, more brightly, more brightly than the Sun
- Lecial categories(어휘 범주) - 내용어
- Noun (명사): puppy, girl, soup, happiness, pillow
- Verb (동사): find, run, sleep, realize, see, want
- Preposition (전치사): up, down, across, into, from, with
- Adjective (형용사): red, big, candid, lucky, large
- Adverb (부사): again, carefully, luckily, very, fairly
- Functional Categories(기능 범주) - 기능어
- Auxiliary (조동사): verbs such as have, and be, and modals such as may, can, will, shall, must
- Determiners (한정사): the, a, this, that, those, each, every
- 품사
- 영어
- Noun, Pronuon, Verb, Adjective, Adverb, Interjection, Preposition, Conjunction
- 한국어
- 명사, 대명사, 동사, 형용사, 부사, 감탄사, 조사, 수사, 관형사
- 참고 (penn treebank tagset)
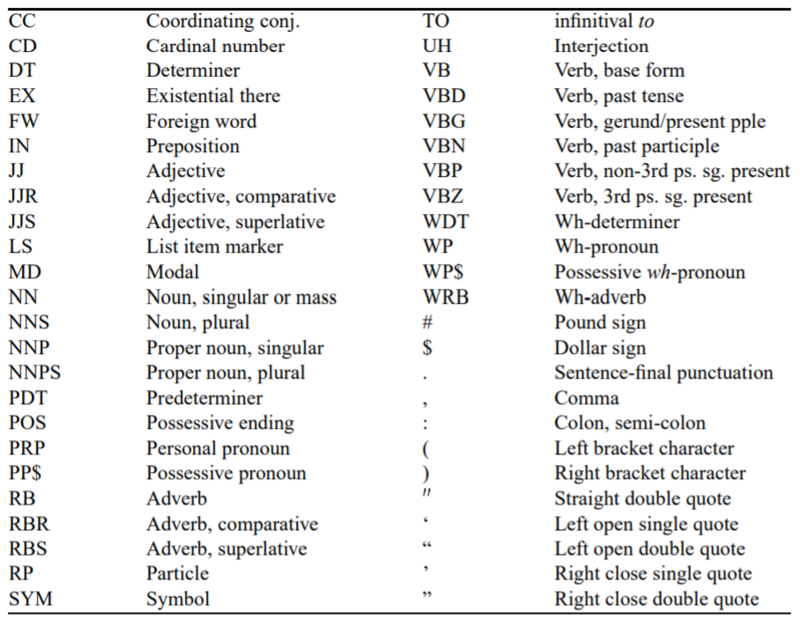
- stanford parser, NLTK → 문장성분을 분류하는 라이브러리
- penn treebank tagset : 영어에서 자연어처리에서 많이 사용되는 품사
5. Phrase Structure Trees
Selection
- 문장이 잘 형성되려면, PS 규칙의 구조 조건에 부합해야 하며 각 구절의 머리부분의 Syntactic(C-selection) 및 semantic(S-selection) 요건도 준수해야 한다.
- 특정 head는 특정 형식의 구성요소를 필요로 하거나 필요로 하지 않는다.(C-selection)
예시
- The verb `find` requires an `NP`: Alex found the ball. - The verb `put` requires both an `NP` and a `PP`: Alex put the ball in the toy box. - The verb `sleep` cannot take a complement: Alex slept. - The noun `belief` optionally selects a `PP`: the belief in freedom of speech. - The `adjective proud` optionally selects a `PP`: proud of herself - 동사는 의미적으로도 구성요소를 선택한다(S-selection) 문법적으로는 맞지만 의미적으로는 부적함
예시
- The beer murdered the lamp (맥주가 램프를 죽였다) murder은 사람에 해당하므로 위 문장은 어색하다 - The beer drank the lamp `drink`의 경우 주체가 마시는 행위를 할 수있는 동물이 와야한다
Phrase Structure Rules
- 요즘은 dependency로 하는 것이다 PS는 예전 방법
- 구조가 단순하고 명료한 장점이 있다
- Examples of the PS rules
- S -> NP VP
- NP -> Det N
- VP -> V NP
- VP -> V
- VP -> V PP
- VP -> V CP
- PP -> P NP
- CP -> C S
- Infinity of Language: Recursive Rule
- 문장을 무한한 구성요소로 생성할 수 있다
-

Structural Ambiguities
구조적 모호성
- 한문장이 2가지 의미를 갖는 경우
- The boy saw the man with the telescope.
→ The boy used the telescope to see the man
→ The boy saw the man who had a telescope.
-

- The boy saw the man with the telescope.
6. Dependency grammer
PS rule보다 현재 더 많이 사용되는 방식
- Phrase structure grammer vs Dependency grammer
- PS 문법의 단점은 구조적으로 복잡하다는 단점이 있다.
- Dependency 문법은 PS 문법보다 단순하다
- PS는 어순이 매우 중요하지만 Dependency 문법에서는 어순에 매우 자유롭다 - 일상생활에서는 어순이 틀리는 경우가 매우 많다
-

- 단어(head)와의 의존관계에 따라 문장 구조가 결정된다.
- Governor(지배소) - 화살표 보내는 단어
- Dependent(의존소) - 화살표 받는 단어
-

Reference
위 글은 데이터 청년캠퍼스 장지원 교수님의 강의를 기반으로 작성되었습니다.
반응형
'AI > 자연어처리(NLP)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 응용 언어학 - 영어(Morphology) (1) | 2021.07.05 |
|---|---|
| 응용 언어학 - 영어(Semantics) (0) | 2021.07.05 |